1.Consider a TCP connection establishment in which a client does an active open and a server does a passive open. Moreover, the acknowledgment from the client (the third TCP segment) is lost.
a) Will the client still be able to send data to the server and why?
b) Will the server receive the data and why, assuming that the data arrives at the receiver correctly?
c) Contrary to what was said in the class about the active/passive close of TCP connections, an HTTP server in fact performs an active close and an HTTP client performs a passive close. There are a few good reasons for this design. However, point out one disadvantage of this design.
TCP在三次握手的时候,第三个数据包丢失了
a, 客户端还会发送数据给服务端么?为什么?
b.服务端是否会接受数据,为什么?数据会正确的达到接收端?
c.大家都知道tcp的主动打开和被动关闭,一个http服务器实际上扮演着主动关闭,客户端去扮演着被动关闭的角色。这样有他的原因,但是,这样有什么缺陷呢?
2.We know that for a 10 Mbps Ethernet segment of 2500m long (a round-trip propagation delay of 51.2微秒), the minimum Ethernet frame length is given by 512 bits (64 bytes).
a) If we upgrade the Ethernet to Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) with the same propagation speed, what is the minimum Ethernet frame length for this case?
b) Is this minimum frame length computed in part (a) acceptable? Explain your answer if it does. Otherwise, suggest a solution to resolve it.
新增题目!
3. Both TCP and UDP use end-to-end checksum to detect errors that escape from error detection from the lower layers (IP and data-link) and errors occurred to the packets while residing in router buffers. Consider the following TCP connection that spans across three data-link networks. Each data-link network provides CRC for error detection. Consider the following two scenarios:
a) Errors have been introduced to the source IP address when the packet is buffered in R1, and there are no other errors.
b) Errors have been introduced to the source IP address in the link between S and R1, and there are no other errors.
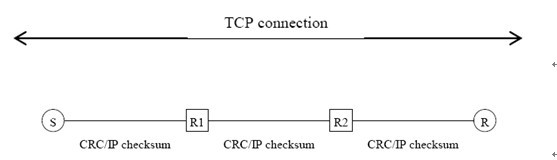
Assume that each CRC can detect the errors with probability pCRC and each 16-bit checksum (for both IP and TCP) can detect the errors with probability pIP. The error detection events are mutually independent. Compute the probability that the errors can be detected for scenarios (a) and (b).
4.Consider an Ethernet network on which host A would like to send a datagram to host B. Host B is on the same network and operational. Instead of using ARP to obtain B’s MAC address, A simply sends the IP datagram using data-link broadcast. Will B receive the datagram? Explain your answer.
同一网段,A发送数据给B,不在arp通告自己mac地址的情况下,简单的讲IP单播数据包链路层广播出去,B会处理么?为什么?
[ 本帖最后由 ctop17 于 2009-8-6 18:27 编辑 ] |